Location
Kaunas, Lithuania

SD card is a device containing a microcontroller and memory chip attached. SD card specific information is stored in internal registers. Each card has a set of information registers : OCR, CID, CSD, RCA, DSR, and SCR. The OCR, CID, CSD and SCR registers carry the card/content specific information, while the RCA and DSR registers are configuration registers storing actual configuration parameters.

Today we will find out what is the SD card CID register and what information it contains.
The Card IDentification (CID) register is 16 bytes (128 bits) code that contains information that uniquely identifies the SD card. CID number is set by the manufacturer and cannot be changed after it is set. As a CID number is unique for each SD card, it is very often used for software licensing and content protection. It can be used as a random number for content encryption, SD locking password generation, or license files. However, if a card does not conform to the specification or a backdoor is found this information could be changed and CID usage for security purposes could be compromised this way!
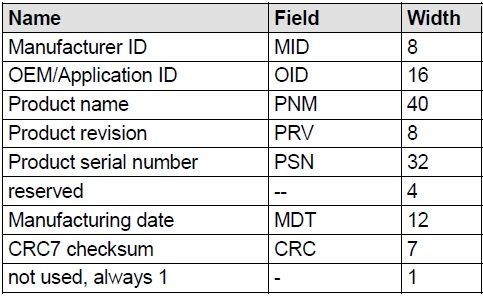
Manufacturer ID (MID) is assigned by the SD Association (SD-3C LLC). It is considered confidential information, so an official list is not published.
Many SD card brands are produced by OEM suppliers, and the MID and OID may reflect this. In some cases, they appear to show the producer of the SD card controller, but not the brand of the SD card. For example, MID 0x27 together with OID – ‘PH’ indicates PHISON controller, but not the card brand, and can be found in many different brands such as Delkin, Integral, Lexar, Patriot, Sony, Verbatim and others, as the Phison Electronics Corporation is one of the common manufacturers for well-known brands.
Manufacturer ID as well as the whole CID is valid and can be trusted only if SD card is original and not counterfeit. Therefore, based on CID number, one cannot be sure that the card is original. If SD card manufacturer ID obviously doesn’t match the label on the card, it’s a first sign that SD card is counterfeit.
Identifies the card OEM and/or the card contents. The OID is controlled and assigned by the SD-3C, LLC. and kept confidential information as MID.
Hi,
Thanks a lot for this good information. If CID is not changable, why after I formatted my VW Navigation Maps, the device is not able to recognize it as original sdcard?
Thanks
Usually navigation unit checks SD card contents and does the contents or some license file matches CID number of SD card. So if you erase maps, navigation unit doesn’t care what CID of this card, is because map data is not available.
Some sd cards don’t have a license file on SD but check whether the CID number is valid for given model/year.
hi,
could you perhaps describe what I need to do to use a normal SD card in a VW RNS315? I have downloaded the new maps from VW website but unfortunately the new (used) passat I just bought, did not come with any navigation SD. If I buy your tool, would it be possible to format a normal SD card to use with RNS315 and load the downloaded maps on it?
thanks